Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
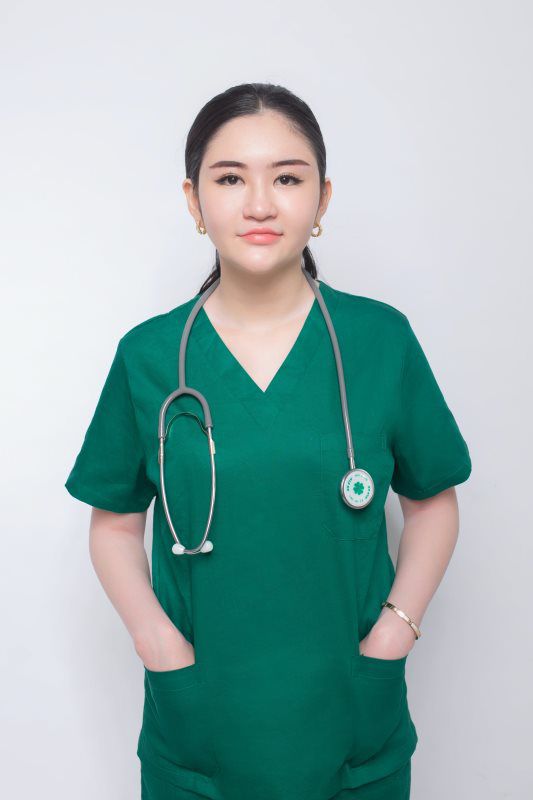
ADHD (attention deficit hyperactivity disorder) is a mental health condition. Attention, ability to sit still and self-control are all affected in people with ADHD due to abnormalities in brain growth and activity.
How Do We Identify ADHD?
Proactive Minds care specialist will often obtain a comprehensive health history, review your symptoms and behaviors in-depth, and perform a physical exam to reach a diagnosis.
Our specialists may employ various techniques, such as examinations and psychological tests.
Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Types
We Seek To Help You Understand Yourself! Per the American Psychological Association (APA), you can show signs of three different sorts. With the Proactive Minds Care team’s expert support, you can effectively cope with whatever type of attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder you have.
Predominantly Inattentive
Predominantly inattentive attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder is sometimes called attention-deficit disorder (ADD).
Short attention span, quickly bored, lack of organization, inclination to daydream, and difficulty following directions are all characteristics of this type of ADHD.
They may also have issues with hyperactivity or impulse control from time to time.
Predominantly Hyperactive-Impulsive ADHD
Predominantly hyperactive-impulsive attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder causes fewer attention symptoms and more hyperactivity issues.
Symptoms include fidgeting, talking constantly, difficulty staying silent, impatience, being perpetually in motion, and making impulsive choices.
Combination ADHD
Combination attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder sufferers have significant symptoms involving both attention and hyperactive-impulsive behaviors.
How We Treat ADHD?
The treatment of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) typically involves a multifaceted approach that may include a combination of behavioral interventions, psychoeducation, and, in some cases, medication. The specific treatment plan is often tailored to the individual's unique needs and may involve collaboration between healthcare professionals, educators, and family members. Here are common components of ADHD treatment:
Behavioral Modification
This involves reinforcing positive behaviors and providing consequences for negative behaviors. It may include strategies like token systems or rewards for completing tasks.
Parent Training
Educating parents on effective parenting strategies and behavior management techniques can help create a supportive environment for the child.
Psychoeducation
Providing information and education about ADHD helps individuals and their families understand the condition better. This includes learning about the nature of ADHD, its impact on daily life, and effective coping strategies.
Psychotherapy
Individual or family therapy can be beneficial in addressing emotional and social challenges associated with ADHD. It provides a supportive space for individuals to discuss their experiences and develop coping skills.
Educational Interventions
Collaborating with educators to implement classroom accommodations and modifications can help support academic success. This may include individualized education plans (IEPs) or 504 plans.
Medication
Stimulant medications (such as methylphenidate or amphetamine-based medications) and non-stimulant medications (such as atomoxetine) are commonly prescribed to help manage symptoms. Medication is typically considered when behavioral interventions alone are insufficient or when symptoms significantly impact daily functioning.
Lifestyle and Environmental Adjustments
Implementing structure and routine in daily life, ensuring adequate sleep, promoting a healthy diet, and minimizing distractions in the environment can contribute to symptom management.